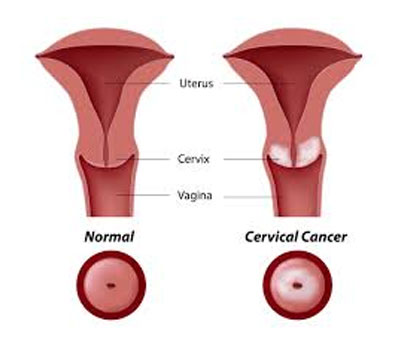
Cervical Cancer is a cancer that originates from the cervix. The cervix is an integral part of the female reproductive system, as it is the lower part of the uterus. In this cancer, the cells grow in abnormal ways and are susceptible to reach other body parts. In women, cervical cancer ranks the forth most common cause of death from cancer, which depicts the risks attached with the disease. Patients may fail to find any early symptoms of the disease; however, the appearance of signs happens at later stage.
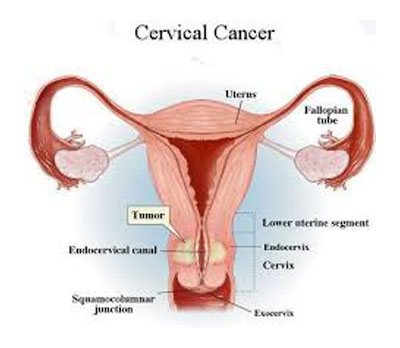
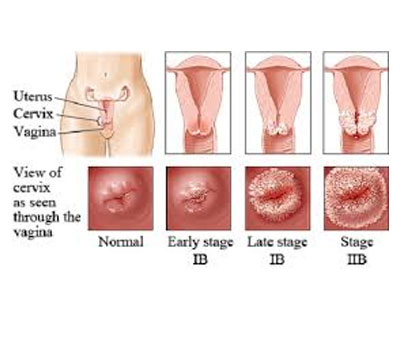
There are basically two types of cervical cancer, and one rare type is also included in the list. Let’s have a look at them all:-
Symptoms are often not visible in the early stages of the cervical cancer, but start appearing at later on. Some of symptoms include: