Transurethral resection (TUR) of the bladder is a surgical technique that is utilized both to analyze bladder tumor and to expel malignant tissue from the bladder. This methodology is additionally called a TURBT (transurethral resection for bladder tumor).
General anesthesia or spinal anesthesia is regularly utilized. Amid TUR surgery, a cystoscope is gone into the bladder through the urethra. An instrument called a resectoscope is utilized to uproot the malignancy for biopsy and to consume with extreme heat any staying growth cells. Bladder growth can return after this surgery, so rehash TURs are once in a while required.
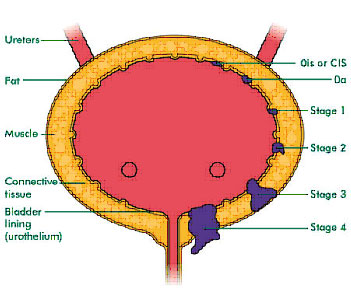
The most common types of bladder tumors include:
Bladder growth signs and indications may include the presence of blood in urine, also known as hematuria. In this, the urine may seem splendid red or cola hued. On the other hand urine may seem ordinary; however blood may be distinguished in an infinitesimal examination of the urine. Other symptoms include:
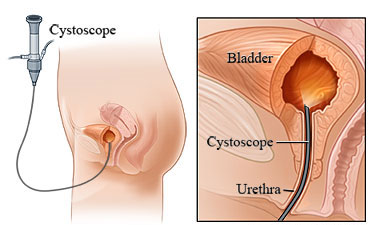
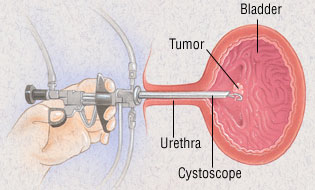
The surgeon will use the equipment called cystoscopy to glimpse inside your bladder. On the off chance that the tumor is in an early stage (shallow) and developing gradually (second rate), it might be evacuated utilizing cystoscopy. Evacuation of a tumor amid cystoscopy is known as transurethral resection (TUR). More often than not, tissue uprooted amid TUR can be examined to check whether more treatment is required.
TUR is normally done in a healing center as an outpatient system. On the off chance that the tumor is expansive, you may be kept in the healing center overnight. You will be given anesthesia so you don't feel torment amid the technique. Provincial anesthesia numbs only the lower piece of your body. On the off chance that you have general anesthesia, you will be totally sleeping.
A cystoscope containing a cutting apparatus is embedded into your bladder through your urethra. The bladder is then analyzed. In the event that tumors are discovered, they are evacuated, if conceivable. A biopsy (test) of both tumor and ordinary looking tissue may be taken. These specimens are taken a gander at under a magnifying instrument for growth cells. Now and again, a laser is utilized to consume a tumor with extreme heat. The laser demolishes tissue, so none is left for biopsy.