The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that produces a milky white substance that makes 30% of semen. Prostate cancer is the disease where cancerous cells start formation in the prostate.
Contrary to other malignant forms, most of prostate cancers don’t grow with a rapid rate, but some do. In some cases, the cancer cells spread to other parts of the body too, bringing more risks from this form of cancer.
Prostate cancer is considered the 2nd most common form of cancer but with a relatively superior rate of survival. This disease has more patients in the developed world.
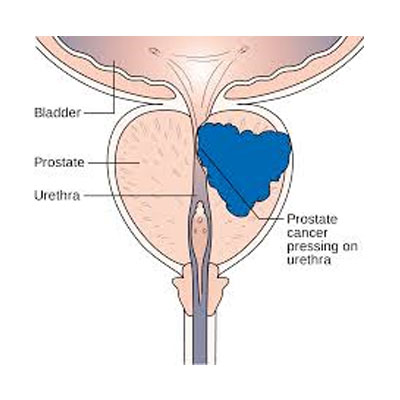
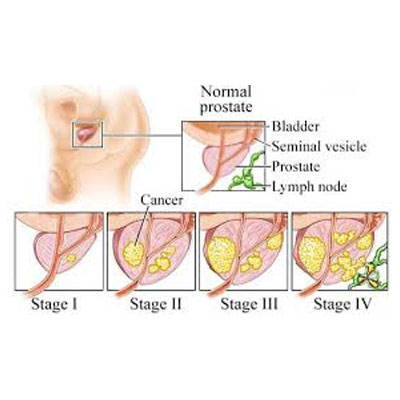
There are many types of prostate cancer. Let’s look at them:-
Acinar Adenocarcinoma – The most common type that originates from gland cells in the prostate.
Ductal adenocarcinoma – It develops in the cells lining the prostate gland’s ducts.
Transitional cell (urothelial cancer) – it starts from the urethra.
Squamous cell cancer – Originates from the flat cells which lie around the prostate gland
Carcinoid of the prostate – It begins from cells of the neuroendocrine system
Small cell cancer – It’s formed of tiny round cells
Sarcoma and sarcomatoid cancer – It begins from muscle cells.
No symptoms are visible at first, but there may be some in later stages of prostate cancer. Let’s have a look at some symptoms:-
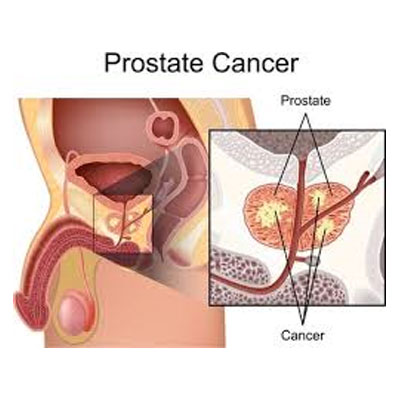
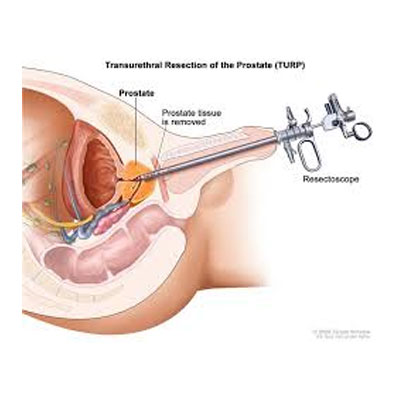
Treatment is not required in cases where low-grade prostate cancer is present as it grows very slowly. More so, age is another factor to consider. There are some side effects related to erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence that make the treatment not feasible.
On the other hand, there are some treatment options that can vary as per the nature of the disease. Before surgery, active surveillance is done. Radiation therapy and cryosurgery may also be needed in specific cases.